June 3, 2021
Quantum Computing with Holes
Scientists found a new and promising qubit at a place where there is nothing.
© Daniel Jirovec
In the world of quantum mechanics, researchers can even make empty space, the lack of something, do their bidding. Scientists from the Katsaros group at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria together with an international team of researchers have now created a new setup to control the absence of electrons in a solid material. They want to use these holes as a basis for a quantum computer.
Quantum computers with their promises of creating new materials and solving intractable mathematical problems are a dream of many physicists. Now, they are slowly approaching viable realizations in many laboratories all over the world. But there are still enormous challenges to master. A central one is the construction of stable quantum bits – the fundamental unit of quantum computation called qubit for short – that can be networked together.
In a study published in Nature Materials and led by Daniel Jirovec from the Katsaros group at IST Austria in close collaboration with researchers from the L-NESS Inter-university Centre in Como, Italy, scientists now have created a new and promising candidate system for reliable qubits.
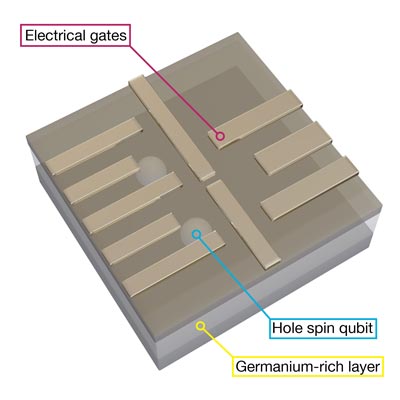
Spinning Absence
The researchers created the qubit using the spin of so-called holes. Each hole is just the absence of an electron in a solid material. Amazingly, a missing negatively charged particle can physically be treated as if it were a positively charged particle. It can even move around in the solid when a neighboring electron fills the hole. Thus, effectively the hole described as positively charged particle is moving forward.
These holes even carry the quantum-mechanical property of spin and can interact if they come close to each other. “Our colleagues at L-NESS layered several different mixtures of silicon and germanium just a few nanometers thick on top of each other. That allows us to confine the holes to the germanium-rich layer in the middle,” Jirovec explains. “On top, we added tiny electrical wires – so-called gates – to control the movement of holes by applying voltage to them. The electrically positively charged holes react to the voltage and can be extremely precisely moved around within their layer.”
Using this nano-scale control, the scientists moved two holes close to each other to create a qubit out of their interacting spins. But to make this work, they needed to apply a magnetic field to the whole setup. Here, their innovative approach comes into play.

Linking Qubits
In their setup, Jirovec and his colleagues cannot only move holes around but also alter their properties. By engineering different hole properties, they created the qubit out of the two interacting hole spins using less than ten millitesla of magnetic field strength. This is a weak magnetic field compared to other similar qubit setups, which employ at least ten times stronger fields.
But why is that relevant? “By using our layered germanium setup we can reduce the required magnetic field strength and therefore allow the combination of our qubit with superconductors, usually inhibited by strong magnetic fields,” Jirovec says. Superconductors – materials without any electrical resistance – support the linking of several qubits due to their quantum-mechanical nature. This could enable scientists to build new kinds of quantum computers combining semiconductors and superconductors.
In addition to the new technical possibilities, these hole spin qubits look promising because of their processing speed. With up to one hundred million operations per second as well as their long lifetime of up to 150 microseconds they seem particularly viable for quantum computing. Usually, there is a tradeoff between these properties, but this new design brings both advantages together.
Publication
Daniel Jirovec, et al. 2021. A singlet triplet hole spin qubit in planar Ge. Nature Material. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-021-01022-2
Funding information
This research was supported by the Scientic Service Units of IST Austria through resources provided by the MIBA Machine Shop and the nanofabrication facility and was made possible with the support of the NOMIS Foundation. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 844511, No. 75441, and by the FWF-P 30207 project. A.B. acknowledges support from the EU Horizon-2020 FET project microSPIRE, ID: 766955. M.B. and J.A. acknowledge funding from Generalitat de Catalunya 2017 SGR 327. ICN2 is supported by the Severo Ochoa program from Spanish MINECO (Grant No. SEV-2017-0706) and is funded by the CERCA Programme / Generalitat de Catalunya. Part of the present work has been performed in the framework of Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona Materials Science PhD program. Part of the HAADF-STEM microscopy was conducted in the Laboratorio de Microscopias Avanzadas at Instituto de Nanociencia de Aragon-Universidad de Zaragoza. ICN2 acknowledge support from CSIC Research Platform on Quantum Technologies PTI-001. M.B. acknowledges funding from AGAUR Generalitat de Catalunya FI PhD grant.



